New Expert Consensus Decision Pathway Updates Guidance on HF Management, Treatment
A newly released ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway (ECDP) focused on the clinical assessment, management and trajectory of patients hospitalized with heart failure (HF) includes revisions to the 2019 version of the document and harmonizes guidance in response to the ACC/AHA Heart Failure Guideline released in 2022 and other ECDP documents addressing chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and chronic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), respectively.
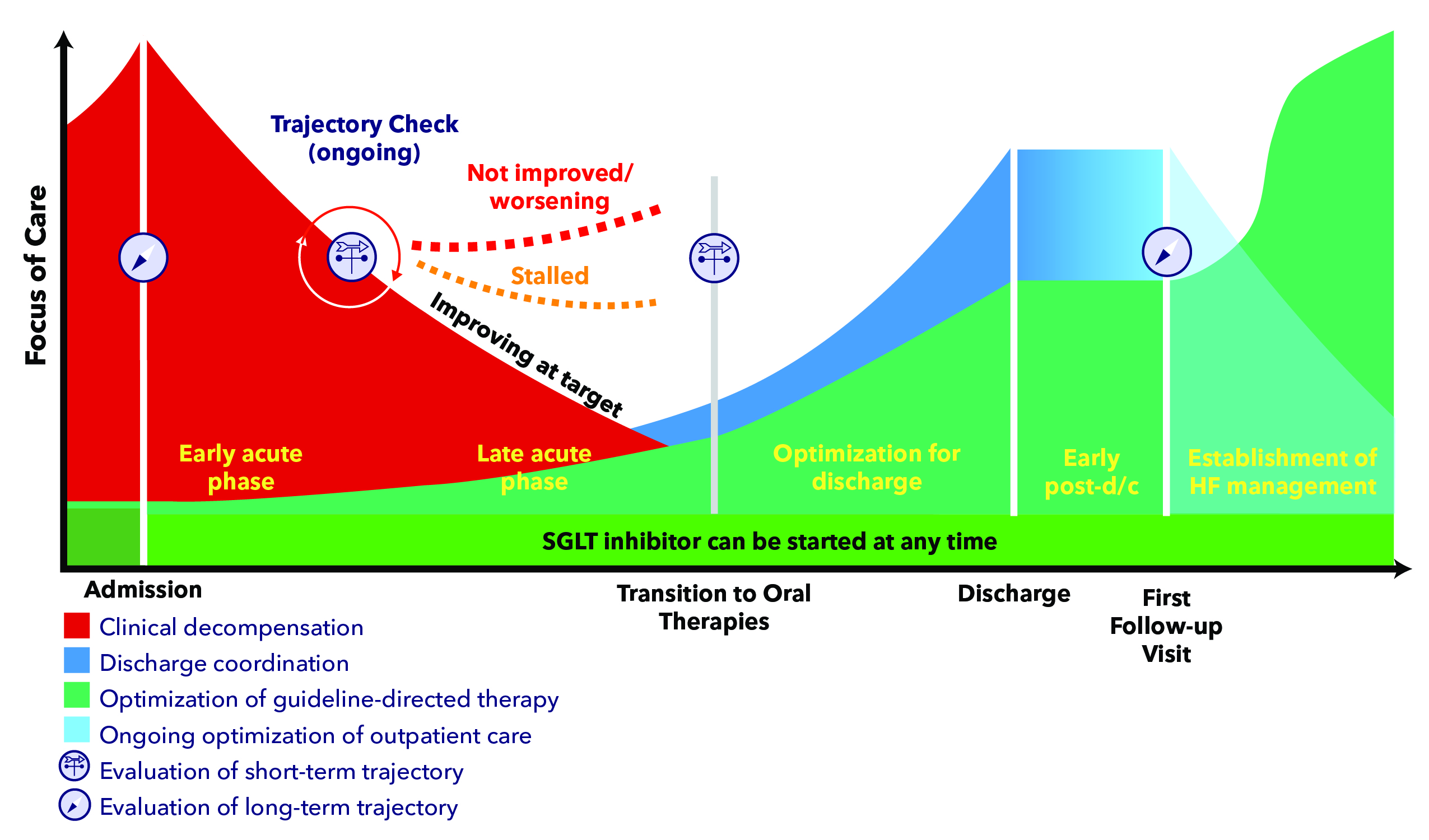
In general, the ECDP led by Writing Committee Chair Steven M. Hollenberg, MD, FACC, and Vice Chair Lynne Warner Stevenson, MD, FACC, retains the general approach of tailoring therapy to the clinical course of HF, from the early acute phase to establishment of HF management. However, the authors note that the pathway "now places increased emphasis on establishing all four pillars of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) for HFrEF in the hospital, when possible, along with ensuring appropriate follow-up to monitor tolerance and continue titration." The ECDP also highlights that SGLT inhibitors can be started at any time during the pathway, including throughout hospitalization regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction.
Other topics addressed by the updated document include decongestion with diuretic and adjunctive therapy and guidance on optimizing neurohormonal modulators during hospitalization for HFrEF. According to the Writing Committee, "decongestion remains an important therapeutic goal in the hospital [and] the sections on diuresis have been updated to include alternative agents and dosing strategies based on new data." The committee also suggests that "strategies for optimization of guideline-directed neurohormonal therapies of beta-adrenergic blocking agents and ARNI/ACE inhibitor/ARB should consider previous tolerance of these therapies, current hemodynamics, and kidney function."
The ECDP also encourages providing patients and referring providers with detailed information regarding diagnoses, discharge regimen and plans – all of which can be used as reference for follow-up phone calls and post-discharge visits, whether in person or conducted via telehealth. Palliative care is also discussed, with guidance provided around advanced care planning, setting goals for care discussions, determining the need for specialist palliative care, caregiver/family support. "There is growing recognition of the importance of palliative care in the management of patients with HF and an emerging evidence base to support its routine incorporation," the authors write.
Clinical Topics: Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies, Acute Heart Failure
Keywords: Heart Failure, Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors, Cardiac Amyloidosis, Diuretics, Hospitalization